Metals & Minerals
Bauxite (Aluminium Ore) Mining
Bauxite is the primary ore of aluminum. Almost all of the aluminum that has ever been produced has been extracted from bauxite. The United States has a few small bauxite deposits but at least 99% of the bauxite used in the United States is imported. The United States is also a major importer of aluminum metal.
Many people are surprised to learn that bauxite is not a mineral. It is a rock composed mainly of aluminum-bearing minerals. It forms when laterite soils are severely leached of silica and other soluble materials in a wet tropical or subtropical climate.
Bauxite does not have a specific composition. It is a mixture of hydrous aluminum oxides, aluminum hydroxides, clay minerals, and insoluble materials such as quartz, hematite, magnetite, siderite, and goethite. The aluminum minerals in bauxite can include: gibbsite Al(OH)3, boehmite AlO(OH), and, diaspore, AlO(OH).
Trans Africa and even globally; the largest single producer of bauxite (aluminium ore) in the world, Cie des Bauxites de Guinée’s (CBG) operation
Geology and reserves

Bauxite deposits are found across much of western and central Guinea, having been formed by the tropical weathering of underlying, aluminium-rich rocks. The deposits are typically close to the surface. Proven reserves total some 2,300Mt with additional probable reserves of 18,600Mt, most of which contains between 40% and 50% aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
“The operation is facing reducing ore grades as high-grade material is mined out.”
CBG and Trans Africa Container ’s operations are based on three main ore zones – Sangarédi, Bidikoum and Silidara, with further resources at the N’danga, Boundou Waade and Paravi deposits. Each deposit contains several different types of ore, varying in both grade and physical properties.
Its existing resource totals over 300Mt grading 51% Al2O3, sufficient to support production at current rates for at least 25 years. Historically, grades in Sangarédi have been 56–58% Al2O3, while ore in Bidikoum averages 50% and Silidara 52%.
In 2006, CBG and Trans Africa Container signed an agreement with the Guinean government and Global Alumina over granting Global Alumina access to some of the CBG and Trans Africa Container bauxite reserve areas. In return, CBG and Trans Africa Container will have future access to some 2,000Mt of bauxite resource that lie outwith its current concession.
Opreations and Projects
Operations are located in the west of Guinea, close to the border with Guinea-Bissau. Since opening in 1973, the operations produced over 260Mt of bauxite for export.
CBG was established in the early 1970s as a 49:51% joint venture between the Guinean government and the Halco partnership, originally comprising a group of international aluminium industry participants. Since 2004, Alcoa and Rio Tinto Alcan have each had a 45% stake in Halco, having gradually bought out most of the other founder members. In mid-1999, the government invited Alcoa to take over management of the project.
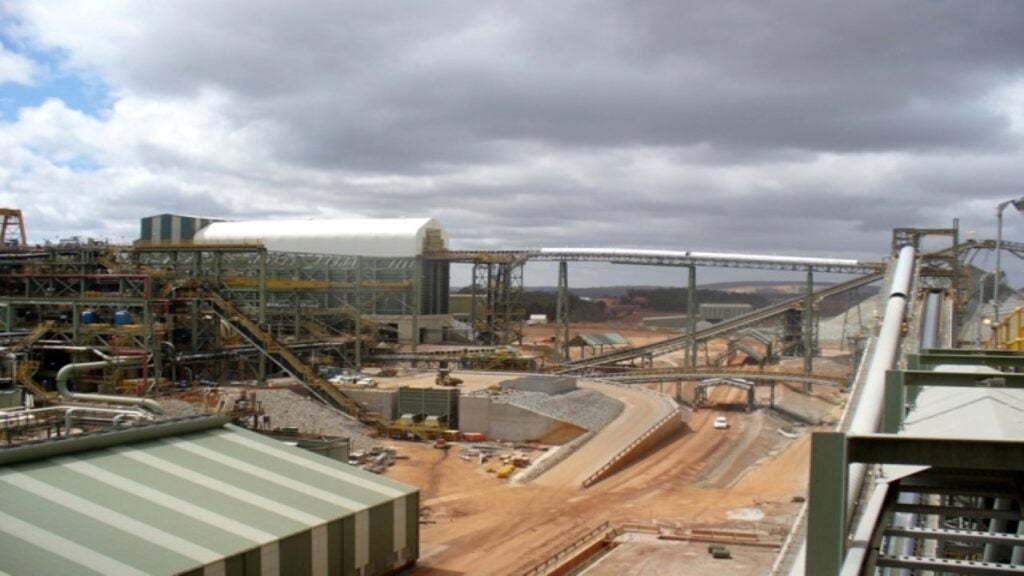
The operations consist of the Kamsar bauxite treatment plant on the West African coast, and a group of open pit mines located 100km inland, centred on the community of Sangarédi. Mine production rose from 12.2Mt in 2001 to just over 14Mt in 2005, with 11.5Mt/y to 12.5Mt/y of bauxite products being shipped from Kamsar. The operation is facing reducing ore grades as high-grade material is mined out.In 2006, Halco reached an agreement with the Guinean Government over the development of a 1.5Mtpa alumina refinery at Kamsar. The original agreement, which was set to expire in November 2008, was extended to November 2012. Alcoa and Rio Tinto Alcan completed the pre-feasibility study in 2008. The commissioning date as per the previous original agreement was scheduled for 2009, with a price tag of at least US$1bn. The same has been rescheduled for 2012. The refinery will have a provision for capacity expansion of up to 4.5Mtpa.
Open pit mining
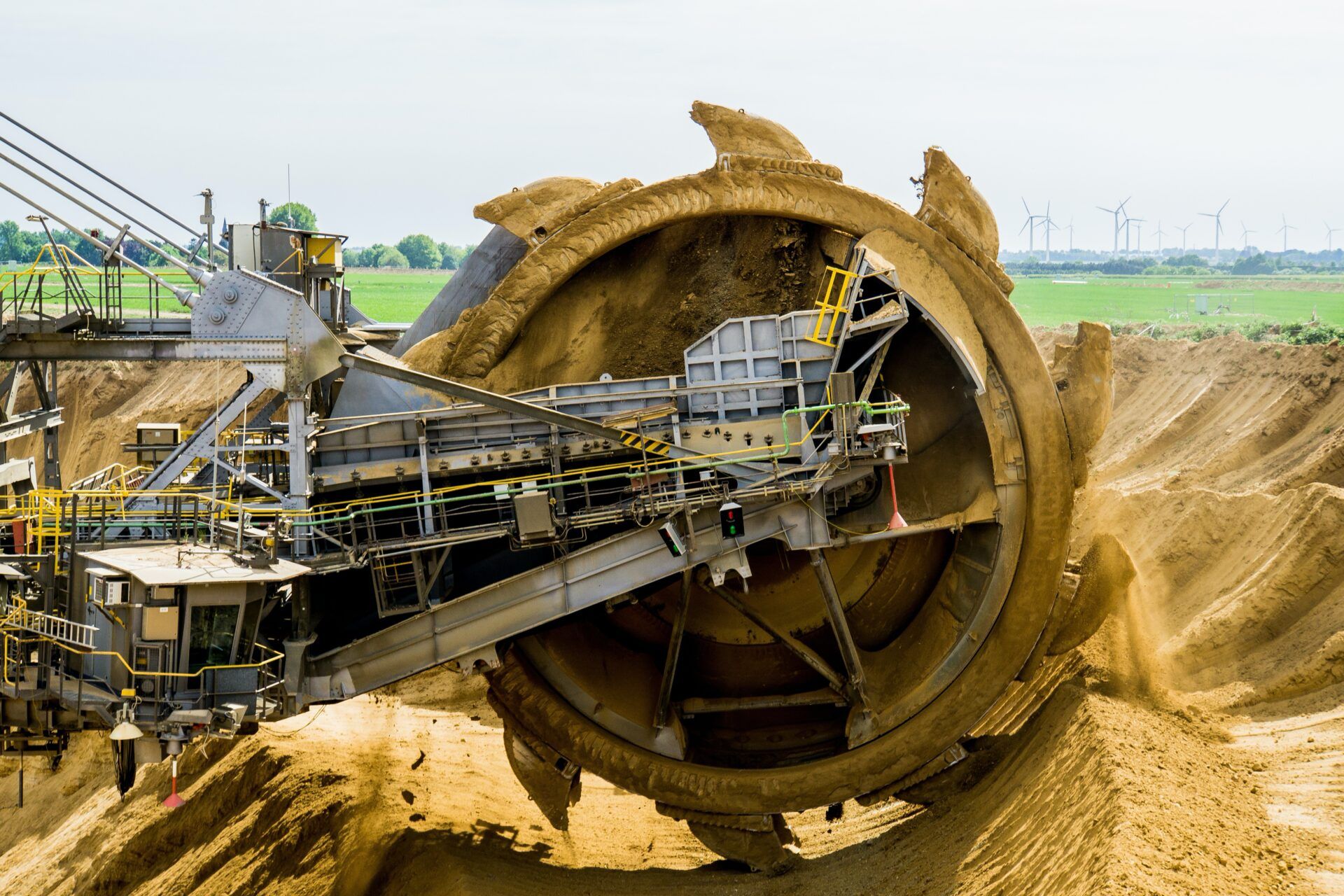


While Sangarédi was the orebody on which CBG and Trans Africa Container ’s operations were founded, today between 85% and 90% of its output of raw bauxite comes from the Bidikoum and Silidara pits. After stripping any thin overburden, the ore is blasted and then loaded using hydraulic excavators into haul trucks for transport to the mine stockpiles.
Bench heights of up to 8m allow most of the ore to be mined in one horizontal pass. The mining fleet consists of Demag H185 excavators, Caterpillar 992C and 992D wheel loaders, and 17 Caterpillar 777B and 777D trucks.
Run-of-mine ore is stockpiled in long piles that run parallel to the mine’s rail sidings, with material from the different pits being tipped in layers to give a consistent blend. The stockpiles are then reclaimed using Caterpillar 992s that dump directly into rail wagons alongside.
“Alcoa has made substantial investments in the rehabilitation of the Kamsar plant, including new belt conveyors and dust-control systems.”
About two hours is needed to load each 100-wagon train, each car carrying around 82t of bauxite. Five or six trains carry ore from the mine to Kamsar each day.

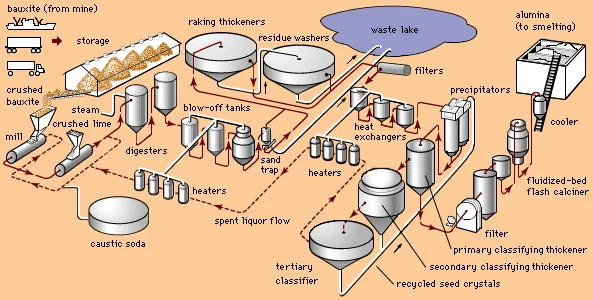
Bauxite processing
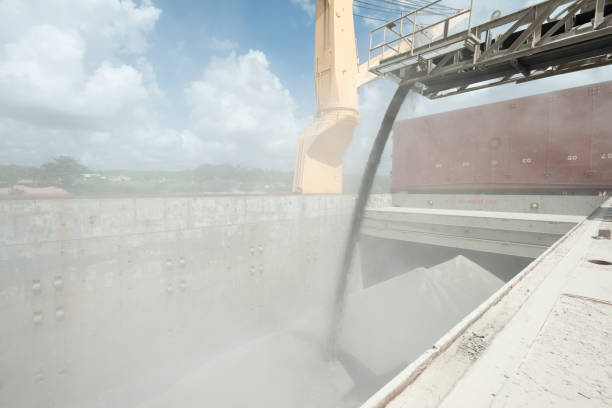
Treatment of the run-of-mine bauxite consists mainly of crushing and drying before shipment. Ore wagons are tipped individually, the material being crushed to –100mm before stockpiling. After reclaim using bucket-wheel stacker-reclaimers, the ore is dried from an average of 12.5% moisture to 6.7% for shipping.
Dried ore is held in a 150,000t-capacity covered stockpile, and is then reclaimed for transport along the plant’s 1.6km jetty to the shiploaders.
The jetty can handle Panamax-sized vessels of up to 60,000dwt, with around 230 such shipments of metallurgical-grade bauxite scheduled per year. In addition, CBG exports low monohydrate and small amounts of calcined bauxite, and has to import all its fuel and equipment spares through its own port facilities.
Alcoa has made substantial investments in the rehabilitation of the Kamsar plant, including new belt conveyors and dust-control systems, with the aim of increasing its export capacity to 13.5Mt/y of bauxite products.
Bench heights of up to 8m allow most of the ore to be mined in one horizontal pass. The mining fleet consists of Demag H185 excavators, Caterpillar 992C and 992D wheel loaders, and 17 Caterpillar 777B and 777D trucks.
Run-of-mine ore is stockpiled in long piles that run parallel to the mine’s rail sidings, with material from the different pits being tipped in layers to give a consistent blend. The stockpiles are then reclaimed using Caterpillar 992s that dump directly into rail wagons alongside.
“Alcoa has made substantial investments in the rehabilitation of the Kamsar plant, including new belt conveyors and dust-control systems.”
About two hours is needed to load each 100-wagon train, each car carrying around 82t of bauxite. Five or six trains carry ore from the mine to Kamsar each day.



Bauxite Formula
Oxide Formula Chemical composition (%wt) Mineralogy
Alumina Al2O3 35 to 65 Gibbsite, diaspore and boehmite
Titania TiO2 0.5 to 8 Rutile and anatase
Silica SiO3 0.5 to 10 Quartz, kaolinite and chalcedony
Calcia CaO nil to 5.5 Magnesite, dolomite and calcite
Ferric oxide Fe2O3 3 to 28 Hematite, siderite and geothite
Importance of Bauxite
Bauxite's Main Applications
In terms of industrial applications, bauxite has a lot of applications. One prominent thing we know about it is that it is very important as the primary ore of aluminium, and we know that this metal is used in a variety of applications. Aside from that, let’s take a look at some of the most common applications for bauxite.
1. Metallurgy
2. In the building material and road accumulates
3. Industries
4. As a catalyst
5. Other Applications
The uses further elaborate as
1. Metallurgy
◦ Bauxite is the prominently used substance to make aluminium.
◦ There are numerous techniques used to extract aluminium from bauxite, such as Bayer Process and Hall-Heroult Process.
◦ The aluminium so obtained utilised extensively in electronic devices, buildings and cars, as well as kitchenware.
◦ This pure aluminium metal may be used in a variety of sectors, including transportation vehicles, building construction, and so on.
2. In the building material and road accumulates
◦ Bauxite is not traditionally used for construction purposes. However, it is often employed in construction projects when alternative materials are unavailable.
◦ As a road aggregate, calcined bauxite can be utilised in some places to prevent accidents.
◦ Bauxite wastes or leftovers known as “red mud” have been utilised to make ceramics with various mechanical characteristics used in the construction of bricks and tiles.
◦ High alumina cement has been proven to be chemically resistant.
◦ Because of these characteristics, it is used in marine shipbuilding.
◦ It is also utilised in precast concrete, water and sewage pipelines, factory chimney construction, and other applications.
3. Industries
◦ It is utilised in a wide range of industries, such as the chemical, refractory, abrasive, cement and steel industries, as well as in the petroleum business.
◦ Bauxite, together with alumina, is used in the production of aluminium compounds, including alumina.
◦ The raw material is used in refractories to make a variety of goods.
◦ It is used in the manufacture of aeroplanes, electric motors, machines, and civil tooling.
◦ Desiccating agents, catalysts, and adsorbents are other uses for it. It is also used in the manufacture of dental cement.
◦ It is also utilised in water purification facilities where alumina works as an absorbent.
◦ Furthermore, bauxite is frequently utilised in the production of paper.
4. Applied as a Catalyst
Alumina (Al2O3) is used as a catalyst in various chemical processes once it has been extracted and purified. For example, activated alumina is used as an adsorbent and catalyst in the synthesis of hydrogen peroxide and polyethene. For the elimination of sulphur, arsenic, and fluoride, it serves as a selective adsorbent. Because it absorbs moisture from the environment, it’s used as a dehydrator to keep items like medicines sterile. Filters made of activated alumina are also used to filter some fluorides. Alumina activated may always be recreated in solution form or reactivated with lye which means pure NaOH.
5. Other Applications
◦ Although bauxite has limited uses, it is widely used in papermaking, water purification, and petroleum refining processes.
◦ Aside from rubber, plastic, paint, and cosmetics, bauxite is also employed in other industries.
'Bauxite rocks are utilised in cement, chemicals, and refractory applications because of their abrasive characteristics. In addition, bauxite's many characteristics and applications continue to make it an intriguing area for research.'
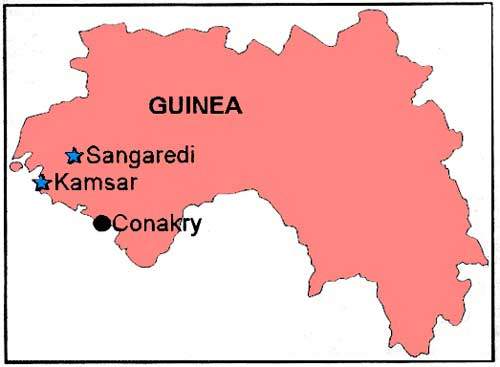
Location Boké, Western Guinea
Our Objectives
Along with our partners we are committed to responsibly sourcing this essential resource .To fully facilitate our output and upgrading standards of living .
Guinea’s bauxite reserves are among the richest in the world, estimated at over 7 billion tons. This abundance positions Guinea as a key supplier to global markets, Developed countries like China that have seen exponential growth in aluminum production.
Geological Overview of Bauxite Deposits in Guinea
The geology of Guinea is highly favorable for bauxite formation due to its tropical climate and geological history. The country’s deposits are primarily located in the Boké region, which features extensive lateritic soils rich in aluminum-bearing minerals. These deposits are typically found near the surface, allowing for open-pit mining methods that are less invasive than underground mining.
The strategic location of these deposits near ports facilitates efficient transportation logistics for exporting bauxite globally. Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu capitalizes on this advantage by maintaining robust supply chains that ensure timely delivery to clients worldwide.
Conclusion: The Future of Bauxite Ore Production in Guinea
As global demand for aluminum continues to rise alongside industrial growth trends, Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu stands poised at the forefront of this dynamic market landscape. With its commitment to sustainable practices and community engagement coupled with advanced extraction technologies, the company not only contributes significantly to Guinea’s economy but also sets a benchmark for responsible mining practices worldwide.
In summary, Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu exemplifies how modern mining operations can thrive while prioritizing environmental stewardship and social responsibility—ensuring that both current needs are met without compromising future generations’ ability to meet theirs.
Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu: Bauxite (Aluminium Ore) Mining Operations
Introduction to Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu
Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu is a pioneering company in the mining sector, specializing in the extraction and processing of bauxite, the primary ore for aluminum production. With a commitment to sustainable practices and technological innovation, Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu plays a crucial role in meeting the global demand for aluminum while ensuring minimal environmental impact.
Understanding Bauxite and Its Importance
Bauxite is an essential raw material used in the production of aluminum, which is one of the most versatile and widely used metals in various industries. The demand for aluminum has surged due to its lightweight properties, resistance to corrosion, and recyclability. It is extensively used in transportation (automobiles, airplanes), construction (windows, doors), packaging (cans, foils), and electrical applications.
The process of extracting aluminum from bauxite involves several steps: mining, refining bauxite into alumina through the Bayer process, and then smelting alumina into aluminum metal via electrolysis. Given this multi-step process, the quality of bauxite mined directly influences the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of aluminum production.
Mining Operations at Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu
Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu operates extensive bauxite mining operations across strategically selected sites rich in high-quality bauxite reserves. The company employs advanced mining techniques that prioritize safety and efficiency while adhering to stringent environmental regulations.
Exploration and Site Selection Before commencing any mining activities, thorough geological surveys are conducted to identify areas with significant bauxite deposits. This exploration phase includes sampling soil and rock formations to assess their composition and quality. The company utilizes state-of-the-art technology such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing tools to enhance accuracy during site selection.
Sustainable Mining Practices Sustainability is at the core of Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu’s operations. The company implements eco-friendly practices throughout its mining processes:
- Minimizing Land Disturbance: By using selective mining techniques that reduce land disruption.
- Rehabilitation Efforts: After mining activities are completed, areas are rehabilitated by replanting native vegetation and restoring ecosystems.
- Water Management: Efficient water usage strategies are employed to minimize waste and protect local water sources.
Extraction Techniques The extraction of bauxite involves both surface mining (open-pit) methods where overburden is removed to access ore deposits near the surface. This method is favored due to its cost-effectiveness compared to underground mining when dealing with shallow deposits.
Processing Facilities Once extracted, bauxite undergoes processing at Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu’s facilities where it is crushed and screened before being transported for refining. The processing plants are equipped with modern machinery designed for optimal efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.
Quality Control Measures Quality control is paramount in ensuring that only high-grade bauxite reaches customers. Regular testing for impurities such as silica, iron oxide, titanium dioxide, and other contaminants ensures compliance with international standards required by aluminum producers.
Logistics and Transportation
Efficient logistics play a critical role in Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu’s operations:
- Transport Infrastructure: The company has invested significantly in transport infrastructure including roads and rail systems that facilitate timely delivery of bauxite to refineries.
- Shipping Capabilities: For international clients, Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu collaborates with shipping companies to ensure safe maritime transport of bulk materials while adhering to all regulatory requirements.
Market Positioning
Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu has established itself as a reliable supplier within the global market for bauxite:
- Client Relationships: Building long-term relationships with major aluminum producers worldwide ensures steady demand for their products.
- Competitive Pricing: By optimizing operational efficiencies through technology integration and sustainable practices, the company can offer competitive pricing without compromising on quality.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu aims to expand its operations further into new regions rich in untapped bauxite reserves while continuing its commitment to sustainability:
- Research & Development: Investing in R&D will allow for innovations that improve extraction methods or develop alternative uses for by-products generated during processing.
- Community Engagement: Engaging local communities through job creation initiatives not only supports regional economies but also fosters goodwill towards mining operations.
Conclusion
Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu stands out as a leader in the field of bauxite (aluminium ore) mining operations through its dedication to sustainable practices, advanced technologies, quality assurance measures, efficient logistics management, strong market positioning, and future-oriented strategies aimed at growth while maintaining environmental stewardship.
By prioritizing these aspects within their operational framework, Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu not only meets current demands but also sets a benchmark for responsible mining practices globally.
With a commitment to sustainable practices and innovative mining techniques, the company aims to meet the growing global demand for bauxite while ensuring minimal environmental impact. This product description will delve into what bauxite is, its uses, and the significance of ore bauxite in industrial applications.
What is Bauxite?
Bauxite is an aluminum-rich ore that serves as the primary source of aluminum production worldwide. It is primarily composed of aluminum oxide minerals such as gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore. The formation of bauxite occurs through the weathering of rocks rich in aluminum silicates under tropical or subtropical conditions. This process results in a residual accumulation of aluminum oxides along with other impurities like iron oxides, silica, and titanium dioxide.
The chemical formula for bauxite can be represented as Al2O3·nH2O, indicating that it contains aluminum oxide combined with water molecules. The specific composition can vary significantly depending on the geographical location and geological conditions under which it was formed.
Bauxite Uses
Bauxite has several critical applications across various industries due to its unique properties:
Aluminum Production: The most significant use of bauxite is in the production of aluminum metal. Approximately 90% of mined bauxite is processed into alumina (aluminum oxide) through the Bayer process before being further refined into aluminum through electrolysis.
Refractory Materials: Bauxite’s high melting point makes it suitable for manufacturing refractory materials used in furnaces and kilns. These materials are essential for industries that require high-temperature processes.
Cement Production: In cement manufacturing, bauxite serves as an important raw material due to its alumina content, which contributes to the formation of calcium aluminate compounds during clinker production.
Chemical Industry: Bauxite is utilized in producing various chemicals such as sodium aluminate, which finds applications in water treatment processes and as a coagulant.
Abrasives: Due to its hardness, bauxite can be processed into abrasives used for grinding and polishing applications.
Construction Materials: Bauxite can also be used as an aggregate in construction projects due to its durability and resistance to weathering.
Fuel Cells: Research is ongoing into using bauxite-derived materials in fuel cells due to their potential catalytic properties.
Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: Some formulations utilize bauxite derivatives for their absorbent properties in cosmetics and personal care products.
Pharmaceuticals: Certain compounds derived from bauxite are explored for their potential medicinal properties.
Glass Manufacturing: Bauxitic materials are sometimes included in glass formulations to enhance certain physical properties.
The versatility of bauxite makes it a crucial mineral resource that supports numerous sectors globally.
Bauxite AR (Augmented Reality)
In recent years, augmented reality (AR) technologies have begun transforming how industries visualize and interact with mineral resources like bauxite. Companies like Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu are exploring AR applications to enhance operational efficiency and safety within mining operations.
With AR tools, miners can visualize underground deposits more accurately, improving exploration efforts by overlaying geological data onto real-world environments. This technology allows for better planning of extraction processes while minimizing environmental disruption by providing insights into optimal mining methods based on real-time data analysis.
Furthermore, AR can facilitate training programs for workers by simulating hazardous situations without exposing them to real dangers on-site. By incorporating AR into their operations, companies can enhance productivity while prioritizing worker safety—a core value at Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu.
Ore Bauxite
Ore bauxite refers specifically to the raw form of bauxite extracted from mines before any processing occurs. The quality and composition of ore bauxite can vary significantly based on its source location; thus, understanding these variations is crucial for efficient processing and utilization.
The extraction process typically involves open-pit mining techniques where overburden (the soil or rock overlaying a mineral deposit) is removed to access the ore beneath it. Once extracted, ore bauxite undergoes several stages of processing:
Crushing and Grinding: The ore is crushed into smaller pieces to increase surface area for subsequent refining processes.
Bayer Process: This widely used method involves mixing crushed ore with sodium hydroxide at high temperatures under pressure to dissolve aluminum-containing minerals while leaving impurities behind.
Clarification: After digestion, the mixture undergoes clarification where undissolved impurities settle out.
Precipitation: Aluminum hydroxide precipitates from the solution upon cooling.
Calcination: Finally, aluminum hydroxide undergoes calcination at high temperatures (around 1000-1100°C) to produce alumina (Al2O3), which can then be reduced to metallic aluminum via electrolysis using Hall-Héroult process.
Understanding the characteristics of ore bauxite—such as its mineral composition and impurity levels—is vital for optimizing these processes and ensuring high-quality alumina production essential for various applications mentioned earlier.
In conclusion, Trans Africa Containers Mining Sarlu plays a pivotal role in harnessing this valuable resource through responsible mining practices that prioritize sustainability while meeting global demands for aluminum production and other industrial uses derived from bauxite ore.
Investments
Related projects

Songwe Hill Rare Earths Project, Malawi, East Africa

Silidara Open Pit . Nord, Boké Prefecture, Boké Region, Guinea

